-
What are dioxins?
Date posted:
-
-
Post Author
dev@edge.studio
1. General
Dioxins belong to a special group of persistent environmental chemicals. Number of studies including those by WHO (World Health Organisation) have shown several risky effects of Dioxins on human health, such as dermal toxicity, immunotoxicity, reproductive effects and teratogenicity, endocrine disruption and carcinogenicity. In terms of dioxin release into the environment, the incineration of solid wastes is the worst anthropogenic source.
2. Family of Dioxins
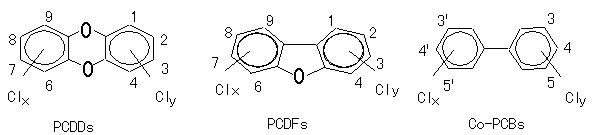
The name dioxin is generally used for the family of structurally and chemically related chlorinated congeners (Fig. 1):
Among some 419 types of dioxin-related compounds identified, only 29 of these are currently considered to have significant toxicity, with 2,3,7,8-TCDD (tetrachlorodibenzo-para-dioxin) being the most toxic.
3. Toxicity Equivalence of Dioxins
The concept of toxic equivalency factors (TEFs) has been used to facilitate risk assessment and regulatory control of exposure to these mixtures. TEF values for individual congeners in combination with their chemical concentration can be used to calculate TEQs (the total 2,3,7,8- TCDD toxicity equivalence quantity) contributed by all dioxin-like congeners in the mixture using the following equation:
Table 1 summarises WHO’s recent assessment of TEFs, which are most commonly used.
Congener
TEF value
Congener
TEF value
Dibenzo-p-dioxins
2,3,7,8-TCDD
1,2,3,7,8-PnCDD
1,2,3,4,7,8-HxCDD
1,2,3,6,7,8-HxCDD
1,2,3,7,8,9-HxCDD
1,2,3,4,6,7,8-HpCDD
OCDD
Dibenzofurans
2,3,7,8-TCDF
1,2,3,7,8-PnCDF
2,3,4,7,8-PnCDF
1,2,3,4,7,8-HxCDF
1,2,3,6,7,8-HxCDF
1,2,3,7,8,9-HxCDF
2,3,4,6,7,8-HxCDF
1,2,3,4,6,7,8-HpCDF
1,2,3,4,7,8,9-HpCDF
OCDF
Table 1: WHO TEFs for human risk assessment
