-
What are the combustion and flue gas properties of Basic Oxygen Steelmaking Gas (BOS)?
Date posted:
-
-
Post Author
dev@edge.studio
1. Introduction
The typical fuel gases used in integrated iron and steelworks are listed in CF62 and introduced in more detail in CF100. This group of industrial fuel gases includes [GLOSS]Basic oxygen steel making gas (BOS gas)[/GLOSS] or [GLOSS]BOS[/GLOSS].
Basic Oxygen Steelmaking Gas is produced as a by-product of the process of decarburising liquid iron in a [GLOSS]basic oxygen furnace[/GLOSS], BOF, vessel. Decarburised liquid iron is called liquid steel.
Basic Oxygen Steelmaking Gas is a medium [GLOSS]calorific value[/GLOSS] fuel gas, which can be used as gaseous fuel in various applications inside and outside the steel plant.
The production, fuel properties and applications of BOS are described in associated Combustion File numbers 219, 245 and 247 respectively.
2. Combustion and flue gas properties of Basic Oxygen Steelmaking Gas
Combustion properties that are important when Basic Oxygen Steelmaking Gas is combusted in industrial furnaces and boilers are the [GLOSS]stoichiometric air requirement[/GLOSS], the [GLOSS]adiabatic flame temperature[/GLOSS], the [GLOSS]flammability limits[/GLOSS], the [GLOSS]auto-ignition temperature[/GLOSS] and the [GLOSS]flue gas[/GLOSS] composition.
To combust Basic Oxygen Steelmaking Gas under stoichiometric conditions, the air requirement is about 1.5 Nm3/Nm3. This is a relative small air requirement (compared with natural gas: 8.5 Nm3/Nm3 to 10.0 Nm3/Nm3) since the main combustible specie in Basic Oxygen Steelmaking Gas is carbon monoxide. This results in a relative high adiabatic flame temperature of about 2000 °C. This is almost equal to the adiabatic flame temperature of a natural gas flame at stoichiometric conditions.
A dry Basic Oxygen Steelmaking Gas – air mixture at ambient temperature and pressure is explosive if the concentration of Basic Oxygen Steelmaking Gas in the mixture is 18.8 – 71.4 vol.% [4].
The auto-ignition temperature of a gas mixture is determined by the lowest auto-ignition temperature of one of the species in the gas mixture. In general, this is the hydrocarbon component with the largest molecule or hydrogen. In a Basic Oxygen Steelmaking Gas – air mixture, the auto-ignition temperature of hydrogen determines the auto-ignition temperature. This is 400°C, which is relatively low compared to the auto-ignition temperature of natural gas: 617°C [5].
In Table 1 the flue gas composition of a stoichiometric Basic Oxygen Steelmaking Gas flame, assuming complete combustion, is presented.
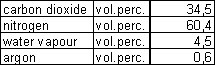
Table 1 Flue gas properties of stoichiometric Basic Oxygen Steelmaking Gas flames, assuming complete combustion
An overview of the gas properties, combustion and flue gas properties of a typical Basic Oxygen Steelmaking Gas is shown in Table 2.
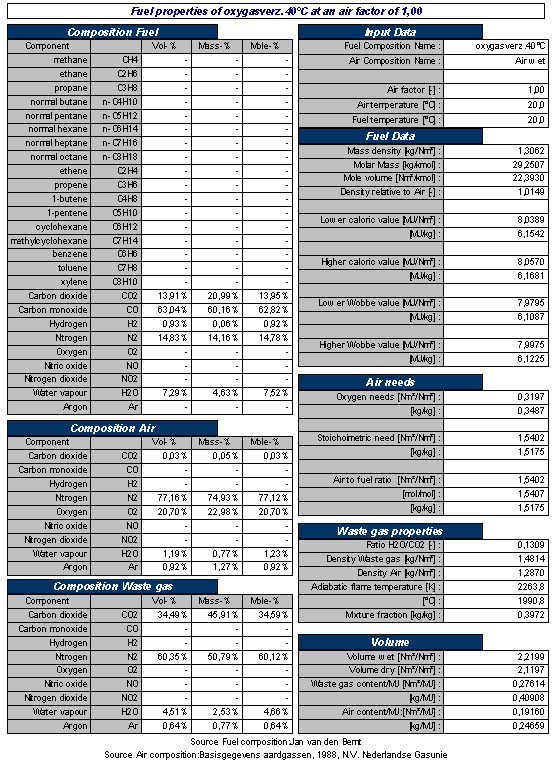
Table 2 Typical example of properties of Basic Oxygen Steelmaking Gas and combustion related properties at stoichiometric combustion
Sources
[1] American Iron and Steel Institute, www.steel.org.
[2] Stubbles, J., The basic oxygen steelmaking BOS process, www.steel.org.
[3] AISE Steel Foundation, 1998, Making, Shaping, and Treating of Steel, 11th Edition, Steelmaking And Refining Volume. Pittsburgh PA
[4] Zabetakis, M.G., Flammability characteristics of combustible gases and vapors, Bulletin 627, Bureau of Mines, 1965.
[5] N.V. Nederlandse Gasunie, Physical properties of natural gases, Groningen, Netherlands, 1980.
[6] Informatie Chemische Stoffen, werkinstructiekaart oxygas, Corus, 2002.
